-
Research Article

-
DMZ 일원 민통선 이북지역의 토지이용에 따른 생태계서비스 및 생태적 가치의 시공간 변화
Spatiotemporal Changes in Land Use, Ecosystem Services, and Ecological Values in the Civilian Control Zone of the Korean DMZ
-
이훈종
Hoonchong Yi
- DMZ 일원은 남북한 분단과 1953년 정전협정을 거치면서 여러 층위의 경계와 구역으로 중첩되어 있다. 이 논문은 민북지역의 토지이용에 따른 생태계서비스의 시공간 변화와 생태적 …
The Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) region has become a multilayered space of boundaries and zones following the division of the Korean Peninsula and …
- DMZ 일원은 남북한 분단과 1953년 정전협정을 거치면서 여러 층위의 경계와 구역으로 중첩되어 있다. 이 논문은 민북지역의 토지이용에 따른 생태계서비스의 시공간 변화와 생태적 가치를 정량적으로 규명한 최초의 학술연구이다. 연구방법은 1980년대 말부터 2000년대 말까지 Landsat 위성영상 기반의 토지피복 데이터 및 글로벌 가치계수를 적용하여 시계열 토지이용, 생태계서비스 유형 및 기능, 그리고 민감도 계수를 산출하였다. 분석결과는 농업지역 확대, 산림 및 초지 감소에 따른 생태계서비스의 동태적인 변화를 나타내고 있다. 민북지역의 생태계서비스 가치는 1980년대 말 연간 $118.39×106 (KRW 165.7×109)에서 2000년대 말 연간 $114.56×106(KRW 160.3×109)으로 변화하였고 해당기간에 3.2% 감소하였다. 생태계서비스의 유형 및 기능별 변화분석에서 공급, 문화, 지지서비스는 각각 0.6%, 3.3%, 3.6% 증가하였다. 이와 대조적으로 조절서비스는 물조절, 침식조절, 기후조절 기능 등을 포함하여 6.5% 감소하였다. 이러한 상반된 유형 및 기능별 분석결과는 민북지역의 토지이용 변화, 조절서비스 교란, 그리고 기후변화 취약성 등 공간구조적 요인이 복합적으로 반영된 것으로 해석할 수 있다. 이와 함께 코스탄자 연구진의 글로벌 가치평가 결과와 연계하여 접경지역 총생산의 편익이전 및 공간할당에 기반한 민북지역의 생태계서비스 가치는 2023년 기준 26.1조원과 34.8조원 사이에서 평가되었다. 해당 가치의 중간 값인 30.4조원은 동일 연도 제주특별자치도의 지역내 총생산을 상회하였고, 한국 국방예산 57조원의 약 53%에 상당하였다. 연구결과는 민북지역의 산림 및 초지의 토지이용 전환, 공급서비스와 조절서비스의 트레이드오프, K-가치계수 및 K-가치평가의 탐구, 그리고 남북한 생태계 지리학 등에 대하여 함의를 갖는다.
- COLLAPSE
The Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) region has become a multilayered space of boundaries and zones following the division of the Korean Peninsula and the 1953 Armistice Agreement. This study represents the first scholarly attempt to quantitatively assess the spatiotemporal changes in ecosystem services and ecological values associated with land use in the Civilian Control Zone (CCZ, also referred to as the ‘Minbuk’ area). The methodology applied Landsat satellite imagery-based land cover data from the late 1980s to the late 2000s, together with global value coefficients, to derive time-series land use, ecosystem service types and functions, and sensitivity coefficients. The analysis revealed dynamic changes in ecosystem services driven by agricultural expansion and the decline of forests and grasslands. The ecological value of ecosystem services in the CCZ decreased by 3.2%, from $118.39×106 (KRW 165.7×109) per year in the late 1980s to $114.56×106 (KRW 160.3×109) per year in the late 2000s. A disaggregated assessment by ecosystem service type and function showed that provisioning, cultural, and supporting services increased by 0.6%, 3.3%, and 3.6%, respectively. In contrast, regulating services, including water regulation, erosion control, and climate regulation, decreased by 6.5%. These contrasting results reflect disturbance of ecosystem functions in the region, likely due to spatial and structural factors associated with land-use changes, disruptions to regulating services, and climate vulnerability. The estimated value of ecosystem services of the CCZ, derived from benefit transfer and spatial allocation based on the global valuation results of Costanza and colleagues, was assessed to range between KRW 26.1 trillion and 34.8 trillion as of 2023. The midpoint value of KRW 30.4 trillion exceeds the Gross Regional Domestic Product (GRDP) of Jeju Special Self-Governing Province in the same year and corresponds to approximately 53% of South Korea’s national defense budget of KRW 57 trillion. These findings carry significant implications for land-use transitions in forests and grasslands of the CCZ, the trade-offs between provisioning and regulating services, the exploration of the Korea-specific value coefficients (K-coefficients) and K-value assessment, and the emerging field of Ecosystem Geography across the Korean Peninsula.
-
DMZ 일원 민통선 이북지역의 토지이용에 따른 생태계서비스 및 생태적 가치의 시공간 변화
-
Research Article
-
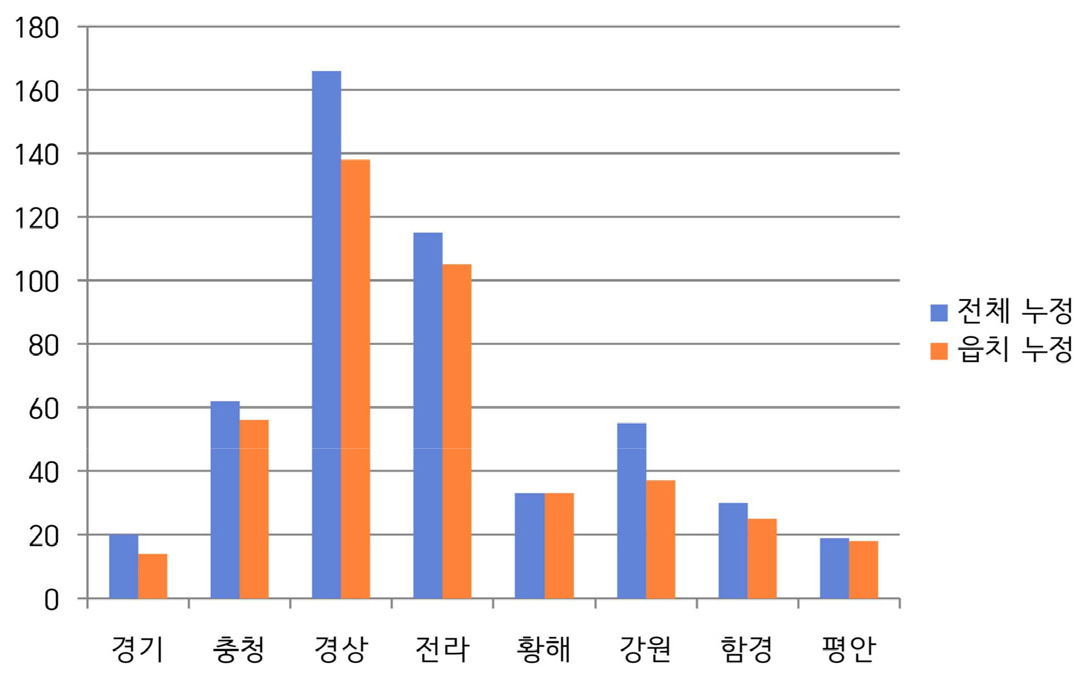
조선전기 ‘읍치(邑治) 누정(樓亭)’의 문화경관적 성격 - 《신증동국여지승람》 수록 읍치 누정의 사례 -
The Cultural Landscape Characteristics of ‘Eupchi(邑治) Pavilion(樓亭)’ in the Early Joseon Period: A Case Study of Pavilions Recorded in the 《Sinjeung Dongguk Yeoji Seungnam》
-
전종한
Jong Han Jeon
- 본 연구는 《신증동국여지승람》에 수록된 읍치(邑治) 누정(樓亭) 기록을 분석하여 조선 전기 읍치 누정의 경관 구성과 장소성을 이해하고 문화경관적 성격을 규명하고자 하였다. 읍치 누정은 …
This study aims to identify the cultural landscape characteristics of ‘Eupchi pavilions’(邑治 樓亭, pavilions of county seats) of the early Joseon …
- 본 연구는 《신증동국여지승람》에 수록된 읍치(邑治) 누정(樓亭) 기록을 분석하여 조선 전기 읍치 누정의 경관 구성과 장소성을 이해하고 문화경관적 성격을 규명하고자 하였다. 읍치 누정은 단순한 건축물이 아닌 공적 기능과 문화적 상징성을 지녔던 곳으로, 지방관의 귀빈 맞이와 유교적 수양, 그리고 백성과의 교감이 이루어지던 현장이었다. 누정의 입지는 읍치의 상징적 중심인 객사 중심의 공간 질서 속에서 이루어졌으며, 그 명칭은 자연 요소로 이루어진 경우조차 덕치(德治)와 인(仁), 풍속의 교화(敎化) 등의 유교적 이념이나 조선의 정신세계를 반영한 매우 상징적이고 함축적인 것이었다. 누정에서 조망된 풍광은 연출된 성격의 차경이기보다는 ‘있는 그대로의 자연과 인간 삶’이었으며, 그것은 자연과 인간이 조우하고, 유교적 이상과 일상적 현실이 교차하는 경관이었다. 조선 전기 읍치 누정은 동아시아의 보편적 누정 문화와 연결되면서도 조선의 자연과 문화, 정치와 학문, 풍속과 도덕이 상호 변환되는 의미의 접점으로서 당대 한반도의 자연환경과 인간 삶의 세계가 상호작용하여 구현한 문화경관이었다.
- COLLAPSE
This study aims to identify the cultural landscape characteristics of ‘Eupchi pavilions’(邑治 樓亭, pavilions of county seats) of the early Joseon period by examining records of those contained in the Sinjeung Dongguk Yeoji Seungnam (Newly Revised Augmented Survey of the Geography of Korea) and analyzing their landscape composition and placeness. Eupchi pavilion was not merely an architectural structure but a place imbued with public functions and cultural symbolism, serving as a venue where local officials entertained distinguished guests, practiced Confucian self-cultivation, and interacted with the local people. The location of pavilions were established within the spatial order centered on the Gaeksa(客舍), the symbolic core of Eupchi, and even when their name were derived from natural elements, they were highly symbolic and suggestive, reflecting Confucian ideals such as Deokchi (德治, virtuous governance), In (仁, benevolence), and Gyowha (敎化, moral cultivation) of local customs, as well as the spiritual worldview of the Joseon period. The scenery viewed from Eupchi pavilion was not a sort of the artificially constructed ‘borrowed landscape’(借景), but rather ‘nature and human life as they truly were’, and was a landscape where nature and humanity converged, and where Confucian ideals intersected with the realities of everyday life. Eupchi pavilion as a meaningful point of convergence where Joseon’s nature and culture of the early Joseon period, while linked to the broader pavilion culture of East Asia, represented a cultural landscape materialized through the interaction between the natural environment and the spiritual worldview of the Korean Peninsula at the time.
-
조선전기 ‘읍치(邑治) 누정(樓亭)’의 문화경관적 성격 - 《신증동국여지승람》 수록 읍치 누정의 사례 -
-
Research Article
-
한국 광업 지역의 산업 경로와 유형
Industrial Paths and Typology of Korean Mining Regions
-
유경식, 구양미
Kyungsik Yu, Yangmi Koo
- 본 연구의 목적은 한국 19개 광업 지역의 산업 경로 분기 과정과 메커니즘을 비교 분석하여 유형화하는 것이다. 이를 위해 ‘위기’를 경로 분기의 ‘결정적 …
The purpose of this study is to comparatively analyze and typologize the processes and mechanisms through which 19 mining regions in Korea …
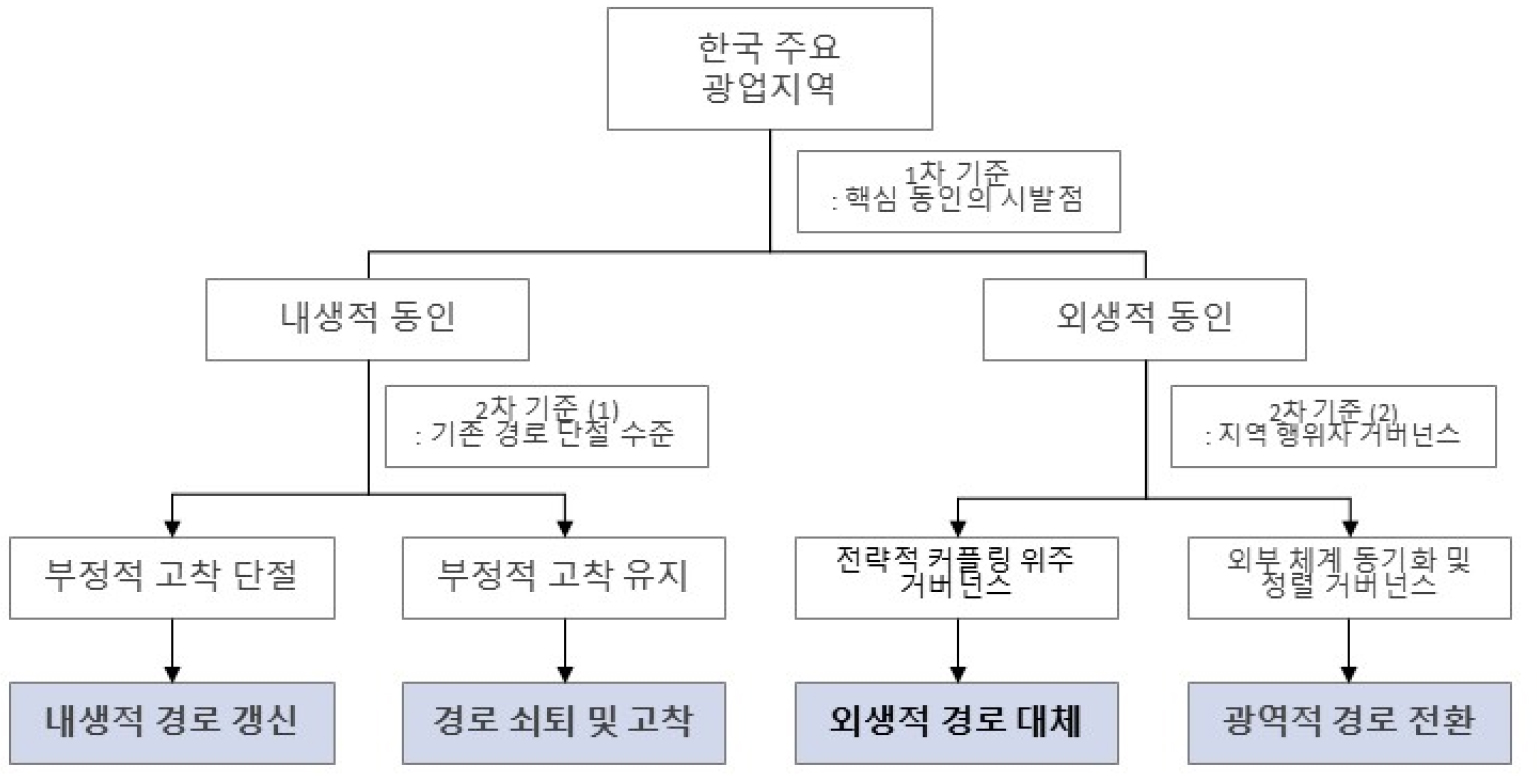
- 본 연구의 목적은 한국 19개 광업 지역의 산업 경로 분기 과정과 메커니즘을 비교 분석하여 유형화하는 것이다. 이를 위해 ‘위기’를 경로 분기의 ‘결정적 국면’으로 설정하고 결정적 국면 이전, 결정적 국면 당시, 그리고 결정적 국면 이후라는 3단계 분석 틀을 통해 각 지역 산업 경로를 추적했다. 분석 결과, 한국 광업 지역의 산업 경로는 ‘내생적 경로 갱신형’, ‘경로 쇠퇴 및 고착형’, ‘외생적 경로 대체형’, ‘광역적 경로 전환형’의 네 가지 유형으로 분류하였다. 각 유형은 지역 경로 발전 핵심 동인의 시발점이라는 1차 기준에 따라 내생적 동인과 외생적 동인으로 구분되었으며, 내생적 동인에 의해 발전한 지역은 부정적 고착의 수준이라는 2차 기준에 따라 분류되었고, 외생적 동인에 의해 발전한 지역은 경로 발전 핵심 거버넌스의 초점을 2차 기준으로 하여 분류되었다. 이러한 결과는 동일한 산업 기반을 가졌더라도 각 지역 산업의 특성과 환경에 따라 위기 대응 방식과 그 결과가 완전히 달라질 수 있음을 보여준다. 본 연구는 지역 쇠퇴에 대한 동일한 정책적 접근의 한계를 지적하고 각 지역 고유의 경로 특성에 기반한 정책 설계 체계 구축의 필요성을 시사한다. 이를 위한 정책으로 자율적인 중간지원조직 기반의 거버넌스를 제시한다.
- COLLAPSE
The purpose of this study is to comparatively analyze and typologize the processes and mechanisms through which 19 mining regions in Korea diverged into different regional industrial paths. To this end, this study establishes ‘crisis’ as the ‘critical juncture’ of path divergence and traces each regional industrial path through a three-stage analytical framework: (1) the period before critical juncture, (2) the critical juncture itself, and (3) the period after the critical juncture. The analysis reveals that the regional industrial paths of Korean mining regions can be classified into four distinct types: ‘Endogenous Path Renewal’, ‘Path Decline and Lock-in’, ‘Exogenous-led Path Creation’, and ‘Macro-regional Path Transition.’ Each type was further distinguished based on a primary criterion: whether the core driver of regional path development originated from endogenous or exogenous factors. Regions developed through endogenous drivers were then classified according to a secondary criterion: the level of negative lock-in. Regions developed through exogenous drivers were classified based on a secondary criterion: the focus of core governance in path development. These results demonstrate that even with identical industrial foundations, crisis response methods and outcomes can differ entirely depending on each region's industrial characteristics and environment. To this end, this research propose a governance model based on autonomous intermediary support organizations.
-
한국 광업 지역의 산업 경로와 유형
-
Research Article
-
코펜하겐을 사례로 한 유럽도시의 뉴어바니즘
European Cities’ New Urbanism: Case study of Copenhagen
-
이자원
Jawon Lee
- 본 연구는 코펜하겐의 핑거플랜 계획을 시기적 변화에 따라 분석해 보았다. 1947년 제안되어 1950-60년대 철도축을 따라 지역계획이 실시된 이후, 1970년 법제화되어 원칙을 보전하며 …
This study examined the evolution of Copenhagen’s Finger Plan across different periods. First proposed in 1947 and implemented through regional planning along …
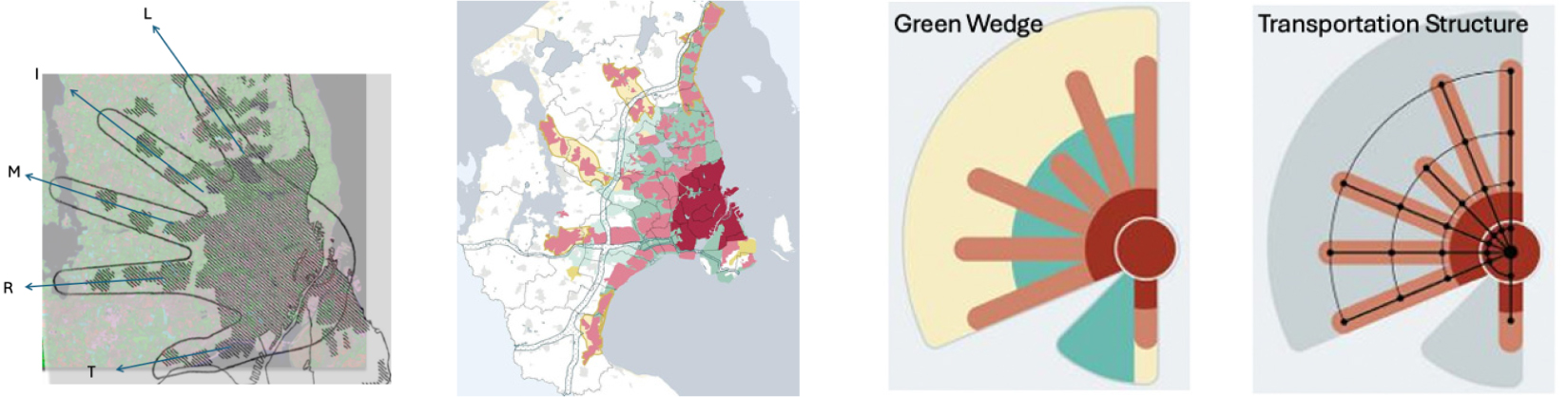
- 본 연구는 코펜하겐의 핑거플랜 계획을 시기적 변화에 따라 분석해 보았다. 1947년 제안되어 1950-60년대 철도축을 따라 지역계획이 실시된 이후, 1970년 법제화되어 원칙을 보전하며 도시계획을 실천하고 있는 장기 도시계획이다. 도심을 손바닥으로, 철도축을 따라 나가는 각 지역을 다섯개의 손가락으로 비유한 핑거플랜은 초기 계획을 1.0이라 칭하고, 이후 21세기 기후변화 대응을 최우선과제로 2.0 세대라 칭하며 유연적으로 환경 변화에 적응하는 계획을 지속하고 있다. 핑거플랜은 전통적 유럽피안 어바니즘의 모델이라고 평가되며 유럽 도시는 물론, 미국 도시에서도 그 원칙이 적용된 사례들이 있다. 1980년대 후반 미국과 캐나다 등에서 제기되었던 커뮤니티를 중심으로 한 공동체 활성화와, 도시의 비지적 확산을 제어하는 전통적 경관 보전의 뉴어바니즘은 코펜하겐이 이미 실행한 도시계획의 상당 부분을 원칙으로 하고 있다. 문화와 역사적 배경을 토대로 한 계획, 공공성이 강화된 사회정책, 접근성을 통한 커뮤니티 강화, 보행로를 우선으로 한 대중교통 체계, 혼합적 토지이용 계획과 압축적 공간활용 계획 등이 1980년대 이후 제시된 뉴어바니즘의 사조와 유사하다. 도시과밀과 지역균형 문제 해결에 대안책이 되고 있는 뉴어바니즘의 원칙은 커뮤니티 기반의 안정적인 성장과 유연적인 대응으로 지속가능한 발전의 실행을 목표로 하기 때문이다. 도시지리학 관점에서 코펜하겐 핑거플랜의 시대별 변화 과정과 각 사례지역의 분석을 통해 뉴어바즘적 도시 관리에 관해 논의하였다.
- COLLAPSE
This study examined the evolution of Copenhagen’s Finger Plan across different periods. First proposed in 1947 and implemented through regional planning along railway corridors in the 1950s and 1960s, it was legally institutionalized in the 1970s and has since been sustained as a long-term planning framework that continues to guide urban development while preserving its foundational principles. Conceptually likening the urban core to a palm and the railway-based development corridors to five fingers extending outward, the plan is commonly referred to as “Finger Plan 1.0” in its original phase. In the 21st century, as climate change emerged as a central planning concern, the model was transformed into a second-generation framework, known as “Finger Plan 2.0,” which demonstrates flexible adaptation to new environmental conditions. Widely regarded as a quintessential model of traditional European urbanism, the Finger Plan has influenced not only European cities but also planning practices in the United States. Its key components—planning rooted in cultural and historical context, socially oriented policies that reinforce publicness, accessibility as a basis for community cohesion, transit systems prioritizing pedestrian routes, and mixed-use, compact land development closely parallel the principles of New Urbanism, a movement that gained traction from the 1980s onward. Addressing urban congestion and regional imbalance, New Urbanism advocates for community-based stability, flexible adaptation, and the practical pursuit of sustainable development. Through a diachronic analysis of the Finger Plan’s evolution and case studies of representative districts, this research seeks to observe and interpret balanced regional development strategies from a geographical perspective.
-
코펜하겐을 사례로 한 유럽도시의 뉴어바니즘
-
Research Article
-
경계 넘기를 통해 본 기지 경계의 투과성과 사회적 구성 - 오키나와 미군 후텐마 비행장의 사례 -
The Porosity and Social Construction of Base Border through Border Crossing: The Case of the U.S. Futenma Air Station in Okinawa
-
박준홍
Jun Hong Park
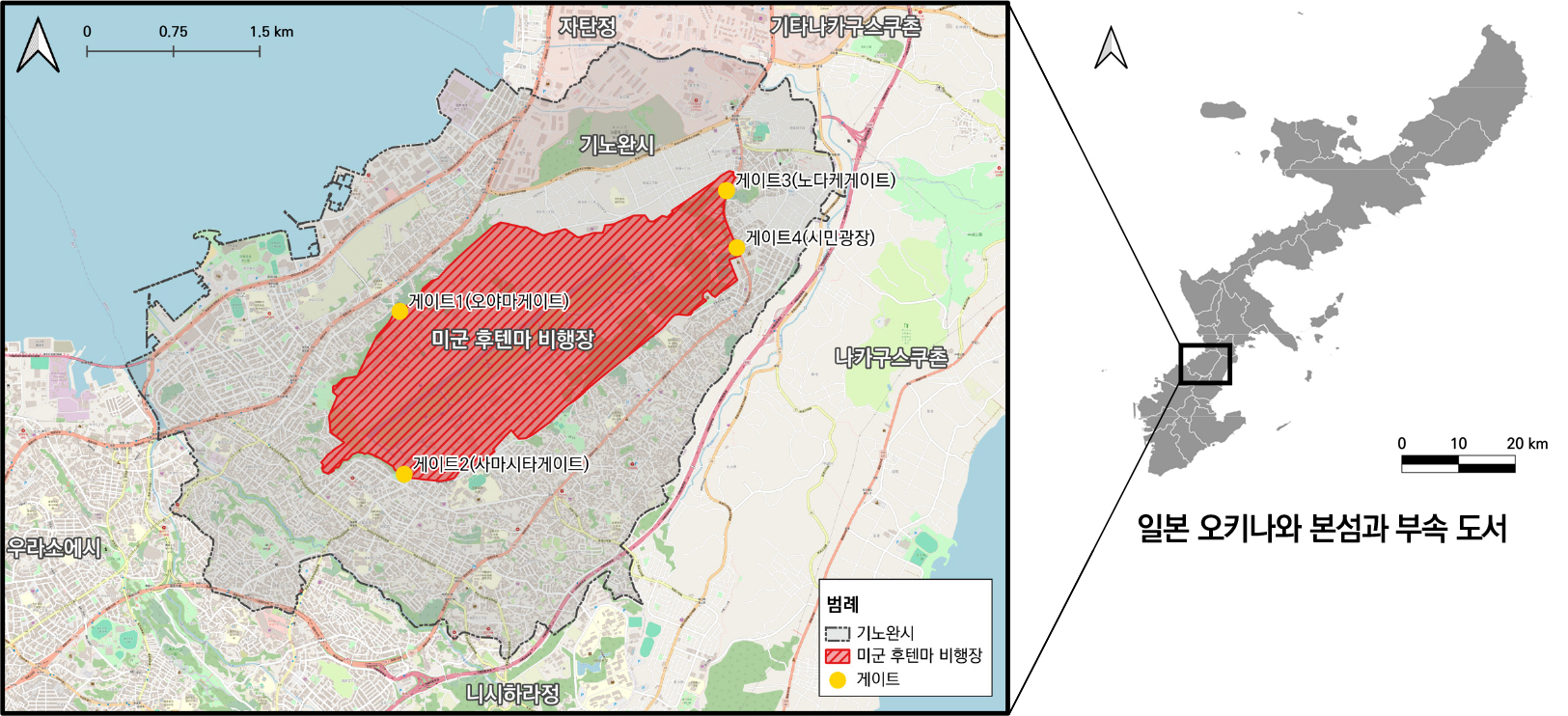
- 본 연구는 오키나와 미군 후텐마 비행장을 사례로, 기지 경계의 투과성과 사회적 의미를 군사기지와 지역사회 사이의 경계 넘기를 통해 살펴보았다. 분석 결과, 기지 …
This study examined the porosity and social meanings of the base border through the lens of border crossing between the U.S. military …
- 본 연구는 오키나와 미군 후텐마 비행장을 사례로, 기지 경계의 투과성과 사회적 의미를 군사기지와 지역사회 사이의 경계 넘기를 통해 살펴보았다. 분석 결과, 기지 내부로의 경계 넘기는 일회적・선별적 투과성으로 나타나며, 미・일・오키나와 및 지역주민 간의 권력관계를 반복적으로 재구조화하는 기제로 작동하고 있었다. 기지로부터의 경계 넘기는 항공기 사고, 소음 발생, 환경오염 물질 배출 등 위험의 외부 확산과 불안의 정동을 동반하며, 이는 경계 내・외부 주체 간의 상반된 경계 인식으로 이어졌다. 본 연구는 군사기지라는 통제된 공간에서도 경계가 투과성을 지니며 권력과 지역사회의 대응이 교차하는 사회공간적 관계 속에서 재구성될 수 있음을 설명하였다. 또한 경계 넘기에 동반된 물질적・비물질적 효과를 신체적・감각적 경험의 층위로 확장해야 함을 강조한다.
- COLLAPSE
This study examined the porosity and social meanings of the base border through the lens of border crossing between the U.S. military base and the local community in Okinawa, focusing on Futenma Air Station. The analysis revealed that border crossing into the base was characterized by occasional and selective porosity, functioning as a mechanism that continuously restructured power relations among the United States, Japan, Okinawa, and local residents. Border crossing from the base, on the other hand, appeared through the external diffusion of risks such as aircraft crashes, noise, and environmental pollution, accompanied by affective experiences of anxiety that fostered conflicting perceptions of the base border between actors inside and outside the border. This study demonstrates that even within the highly controlled space of a military base, the base border possesses porosity and is continually reconstructed within socio-spatial relations where power and local responses intersect. Furthermore, it emphasizes the need to extend the material and immaterial effects of border crossing to the bodily and sensory dimensions of experience.
-
경계 넘기를 통해 본 기지 경계의 투과성과 사회적 구성 - 오키나와 미군 후텐마 비행장의 사례 -
-
Research Article
-
서울시 장애인콜택시의 지역 간 접근성 격차 완화를 위한 차량 재배치 방안
Vehicle Reallocation Strategies to Reduce Regional Accessibility Disparities in Seoul's Wheelchair Accessible Call Taxi Services
-
임희수, 최진무
Heesoo Rhim, Jinmu Choi
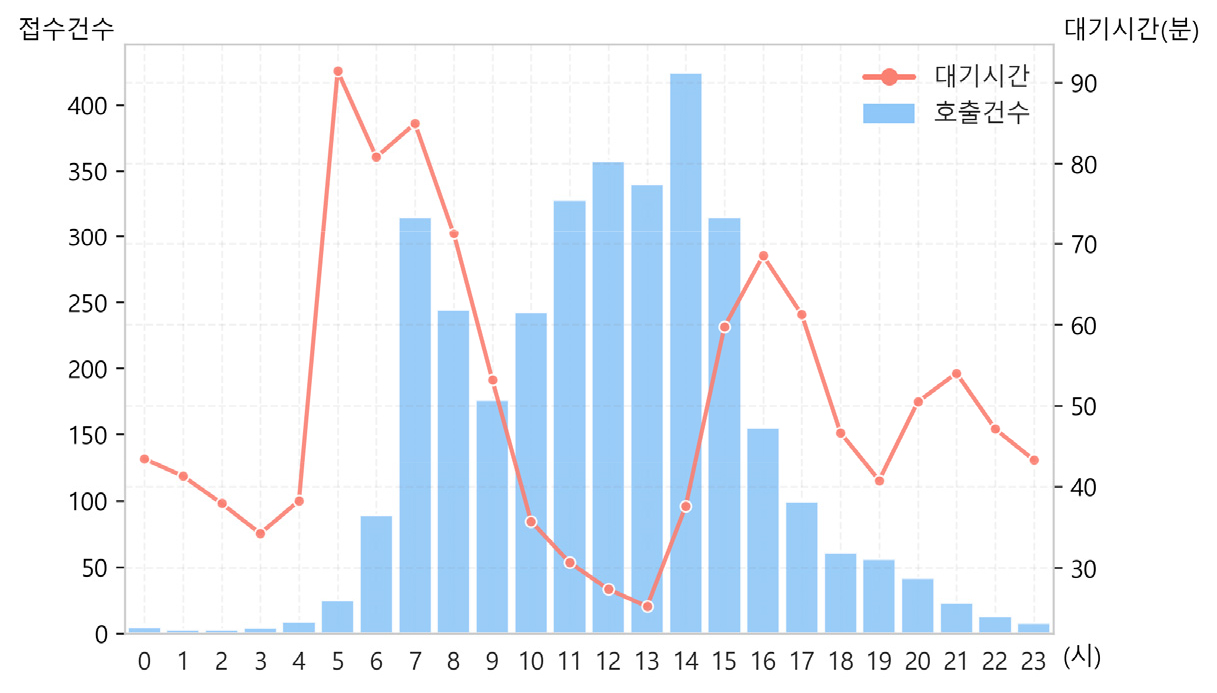
- 서울시 장애인콜택시는 교통 취약계층의 이동권을 지원하는 필수 서비스이나 지역 간 대기시간 격차로 인한 서비스 불평등 문제가 지속되고 있다. 이를 위해 본 연구는 …
Seoul's wheelchair accessible call taxi is an essential service supporting the mobility rights of transportation-vulnerable groups, yet persistent service inequality issues arise …
- 서울시 장애인콜택시는 교통 취약계층의 이동권을 지원하는 필수 서비스이나 지역 간 대기시간 격차로 인한 서비스 불평등 문제가 지속되고 있다. 이를 위해 본 연구는 서울시 장애인콜택시를 대상으로 Two-Step Floating Catchment Area(이하 2SFCA) 기법을 활용하여 공간적 접근성을 정량적으로 평가하고 이차계획법(Quadratic Programming, QP)을 사용하여 접근성 불평등을 최소화하는 차고지별 최적 차량 배치를 도출하고자 하였다. 연구에서는 기존 차고지를 유지하면서 현행 차량 배치, 차량 수 조정 배치, 차량 증차, 증차 후 재배치의 네 가지 시나리오를 설정하고 비교·분석하였다. 분석 결과, 단순 재배치만으로도 수요 가중 표준편차, 변동계수, 지니계수가 개선되어 지역 간 접근성 격차가 완화되었으며 차량 증차와 재배치를 병행할 경우 접근성의 절대적 수준과 형평성이 동시에 향상됨을 확인하였다. 본 연구는 장애인콜택시 서비스의 공간적 형평성을 높이기 위한 정책적 기초자료를 제공하며 제한된 자원을 효율적으로 배분할 수 있는 최적화 방법론을 제시한다는 점에서 의의를 가진다.
- COLLAPSE
Seoul's wheelchair accessible call taxi is an essential service supporting the mobility rights of transportation-vulnerable groups, yet persistent service inequality issues arise due to regional disparities in waiting times. To address this, this study quantitatively assessed the spatial accessibility of Seoul's wheelchair accessible call taxi using the Two-Step Floating Catchment Area (2SFCA) technique. It then employed Quadratic Programming (QP) to derive the optimal vehicle allocation per garage location, aiming to minimize accessibility inequality. The study maintained existing garages while setting and comparing four scenarios: current vehicle allocation, adjusted vehicle allocation, vehicle expansion, and reallocation after expansion. Analysis confirmed that simple reallocation alone improved the demand-weighted standard deviation, coefficient of variation, and Gini coefficient, mitigating regional accessibility gaps. Concurrent vehicle expansion and reallocation simultaneously enhanced both the absolute level of accessibility and equity. This study is significant as it provides foundational policy data to enhance the spatial equity of paratransit services for persons with disabilities and proposes an optimization methodology for efficiently allocating limited resources.
-
서울시 장애인콜택시의 지역 간 접근성 격차 완화를 위한 차량 재배치 방안
-
Research Article
-
해안사구 생태계서비스 정량평가를 위한 생태계서비스 평가지도의 적용 가능성 분석
Analysis of the Applicability of Ecosystem Services Assessment Maps for the Quantitative Evaluation of Coastal Dune Ecosystem Services
-
정필모, 최철현
Pilmo Jung, Chulhyun Choi
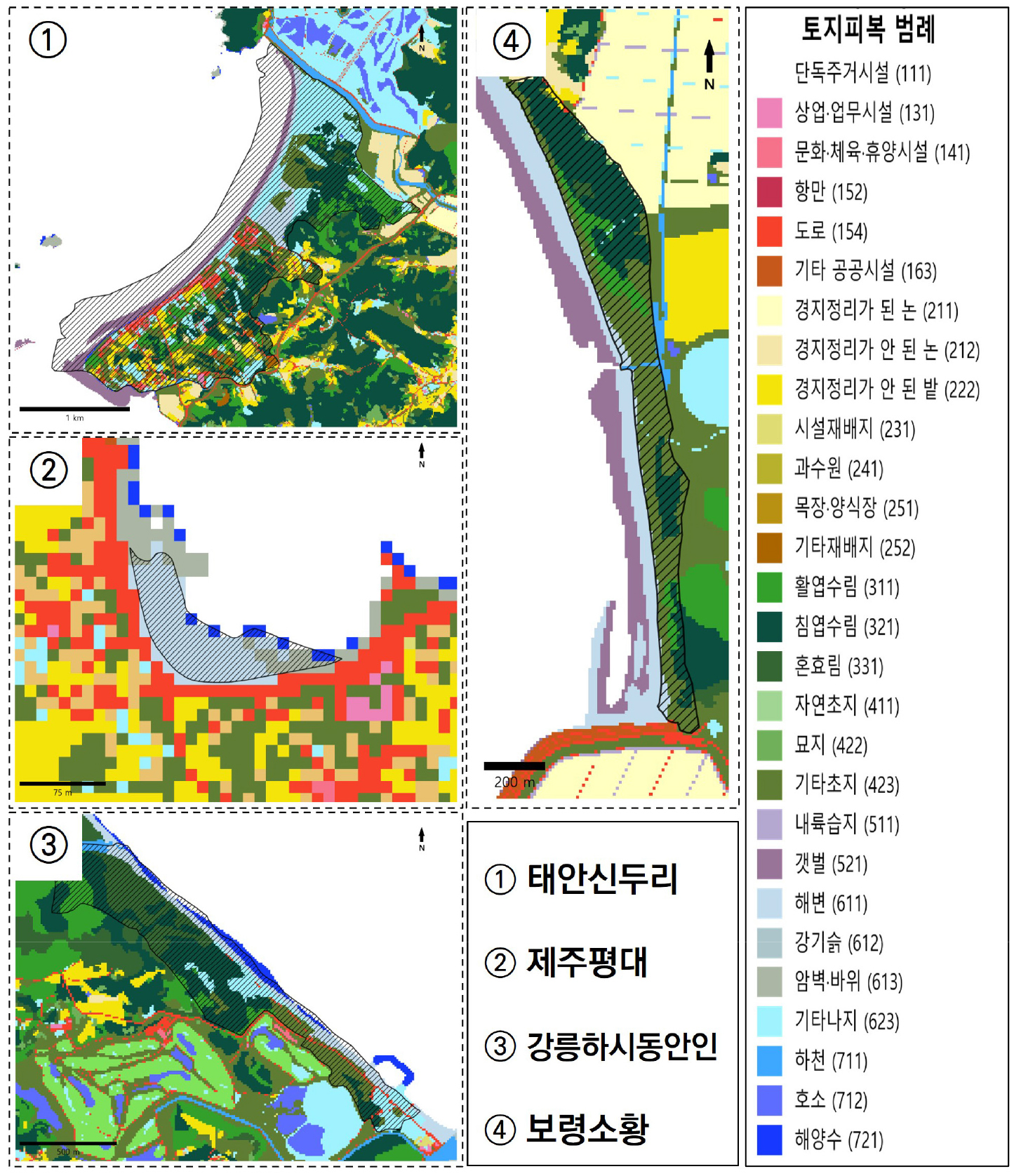
- 본 연구는 국내 189개 해안사구를 대상으로 토지피복도와 InVEST를 활용하여 제작된 생태계서비스 평가지도의 적용 가능성을 정량적으로 검증하였다. 공간자료 중첩 분석을 통해 사구별 생태계서비스 …
This study quantitatively verified the applicability of the ecosystem service assessment map, which was created using the Land Cover Map and InVEST, …
- 본 연구는 국내 189개 해안사구를 대상으로 토지피복도와 InVEST를 활용하여 제작된 생태계서비스 평가지도의 적용 가능성을 정량적으로 검증하였다. 공간자료 중첩 분석을 통해 사구별 생태계서비스 평가 결과의 유효성을 식별하였고, 항목별 적용성을 비교하였다. 분석 결과, 탄소저장·대기조절·열섬저감·기저유량기여도 항목은 대다수 사구에서 신뢰도 높은 평가가 가능하였으며, 수질정화·생태관광 항목은 해안사구의 생태 특성(토양과 습지, 해상도 제약)으로 인해 적용의 한계가 확인되었다. 또한 토지피복도에 사빈과 조간대 지역이 누락되는 공간적 한계가 평가 결과에 영향을 미치고 있음을 밝혔다. 이러한 한계를 보완하기 위해 정기적 식생조사에 기반한 식생도-토지피복 자료 융합 방안을 제안하였다. 본 연구는 해안사구 생태계서비스의 정량 평가 적용 가능성을 확인함과 동시에, 전국 단위 공간자료 활용의 제약 및 개선 조건을 제시함으로써 향후 해안 생태계서비스 평가 및 관리 정책 수립의 기초 자료로 활용될 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
- COLLAPSE
This study quantitatively verified the applicability of the ecosystem service assessment map, which was created using the Land Cover Map and InVEST, to 189 coastal dunes in South Korea. Through spatial data overlay analysis, the effectiveness of the ecosystem service assessment results for each dune was identified, and the item-specific applicability was compared. The analysis showed that items such as carbon storage, air purification, urban heat island mitigation, and baseflow contribution allowed for highly reliable assessment in most dunes. However, water purification and ecotourism items were found to have limitations in applicability due to the ecological characteristics of coastal dunes (soil and wetlands, resolution constraints). Furthermore, it was revealed that a spatial limitation—the omission of beach and tidal flat areas in the Land Cover Map—was influencing the assessment results. To compensate for these limitations, a method for integrating vegetation maps and land cover data based on regular vegetation surveys was proposed. This study confirmed the applicability of quantitative assessment for coastal dune ecosystem services and, by presenting constraints and improvement conditions for the utilization of national spatial data, is expected to be utilized as fundamental data for future coastal ecosystem service assessment and management policy establishment.
-
해안사구 생태계서비스 정량평가를 위한 생태계서비스 평가지도의 적용 가능성 분석
-
Research Article
-
무의식의 공간 - 감정, 정동, 정신분석지리학으로의 초대 -
The Space of the Unconscious: An Invitation to Emotional, Affective, and Psychoanalytic Geography
-
지명인
Myung In Ji
- 2000년대 영미권 지리학계의 ‘감정적 전환’ 이후, 국내 지리학계에서도 감정과 정동에 대한 논의가 양적·질적 성장을 거듭해 왔다. 그러나 두 개념의 미묘한 차이와 그로 …
Since the ‘emotional turn’ in Anglo-American geography during the 2000s, discussions on emotion and affect within Korean geography have achieved significant quantitative …
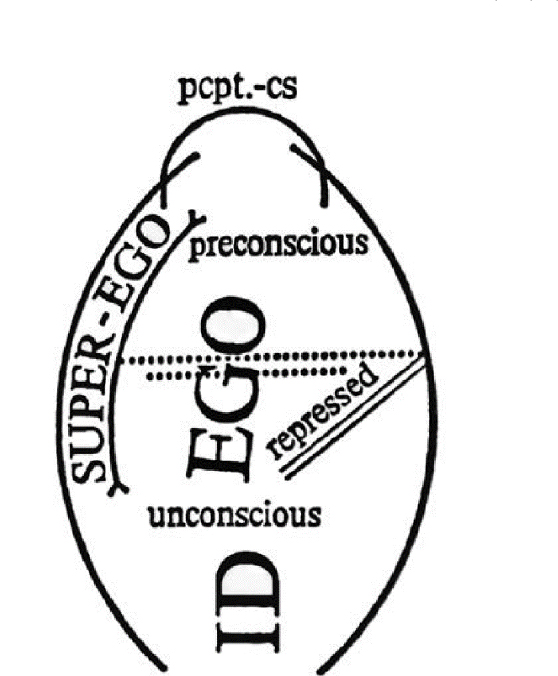
- 2000년대 영미권 지리학계의 ‘감정적 전환’ 이후, 국내 지리학계에서도 감정과 정동에 대한 논의가 양적·질적 성장을 거듭해 왔다. 그러나 두 개념의 미묘한 차이와 그로 인한 인식론적·존재론적 논쟁들은 여전히 충분히 조명되지 못한 실정이다. 본 논문은 이러한 학술적 간극에 응답하여 감정과 정동 연구의 지리학적 계보를 비판적으로 고찰하는 한편, 이 두 힘이 현실 세계에서 작동하는 방식을 독해하기 위한 렌즈로서 정신분석 이론을 제안한다. 구체적으로 본 논문은 프로이트의 ‘정신 모델’과 라캉의 ‘주체성의 위상학’을 공간적으로 분석함으로써, 의식/무의식, 주체/타자, 안/밖이 끊임없이 뒤엉키며 생성하는 물질적-심리적 시공간을 탐색한다. 특히 정신분석지리학의 사례 연구들에 대한 면밀한 검토를 통해, 감정과 정동의 표면 아래에서 작동하는 무의식이 어떻게 인간-공간의 위상적 역동을 매개하는지 규명한다. 이를 통해 본 논문은 정신분석이 추상적 이론이 아니라, 현실의 사회공간적 갈등과 모순을 이해하는 실천적이고 유의미한 지리학적 렌즈임을 입증한다.
- COLLAPSE
Since the ‘emotional turn’ in Anglo-American geography during the 2000s, discussions on emotion and affect within Korean geography have achieved significant quantitative and qualitative growth. However, the subtle nuances between these two concepts and the ensuing epistemological and ontological debates remain insufficiently illuminated. Responding to this academic gap, this article critically reviews the geographical genealogy of emotion and affect research, while proposing psychoanalytic theory as a lens to decipher the mechanisms by which these two forces operate in the real world. Specifically, by providing a spatial reading of Freud’s ‘models of the psyche’ and Lacan’s ‘topology of subjectivity,’ this article explores the material-psychological spacetime generated where the conscious/ unconscious, subject/other, and inside/outside are ceaselessly intertwined. In particular, through a rigorous examination of case studies in psychoanalytic geography, it elucidates how the unconscious, operating beneath the surface of emotion and affect, mediates the topological dynamics between humans and space. Ultimately, the article demonstrates that psychoanalysis is not merely an abstract theory, but a practical and meaningful geographical lens for understanding socio-spatial conflicts and contradictions in reality.
-
무의식의 공간 - 감정, 정동, 정신분석지리학으로의 초대 -
-
Research Article
-
동해/일본해 표기 이슈에 대한 비판지명학의 시각
The East Sea/Sea of Japan Naming Issue: A Critical Toponymy Perspective
-
주성재
Sungjae Choo
- 본 연구는 동해/일본해 표기 문제를 둘러싼 새로운 학술적 접근의 필요성에 주목하고, 선행 연구에서 지속가능한 지명 사용의 핵심 화두로 제기된 비판지명학의 관점을 적용하고자 …
This study originates from the recognition that a new scholarly approach is needed to address the East Sea/Sea of Japan naming issue, …
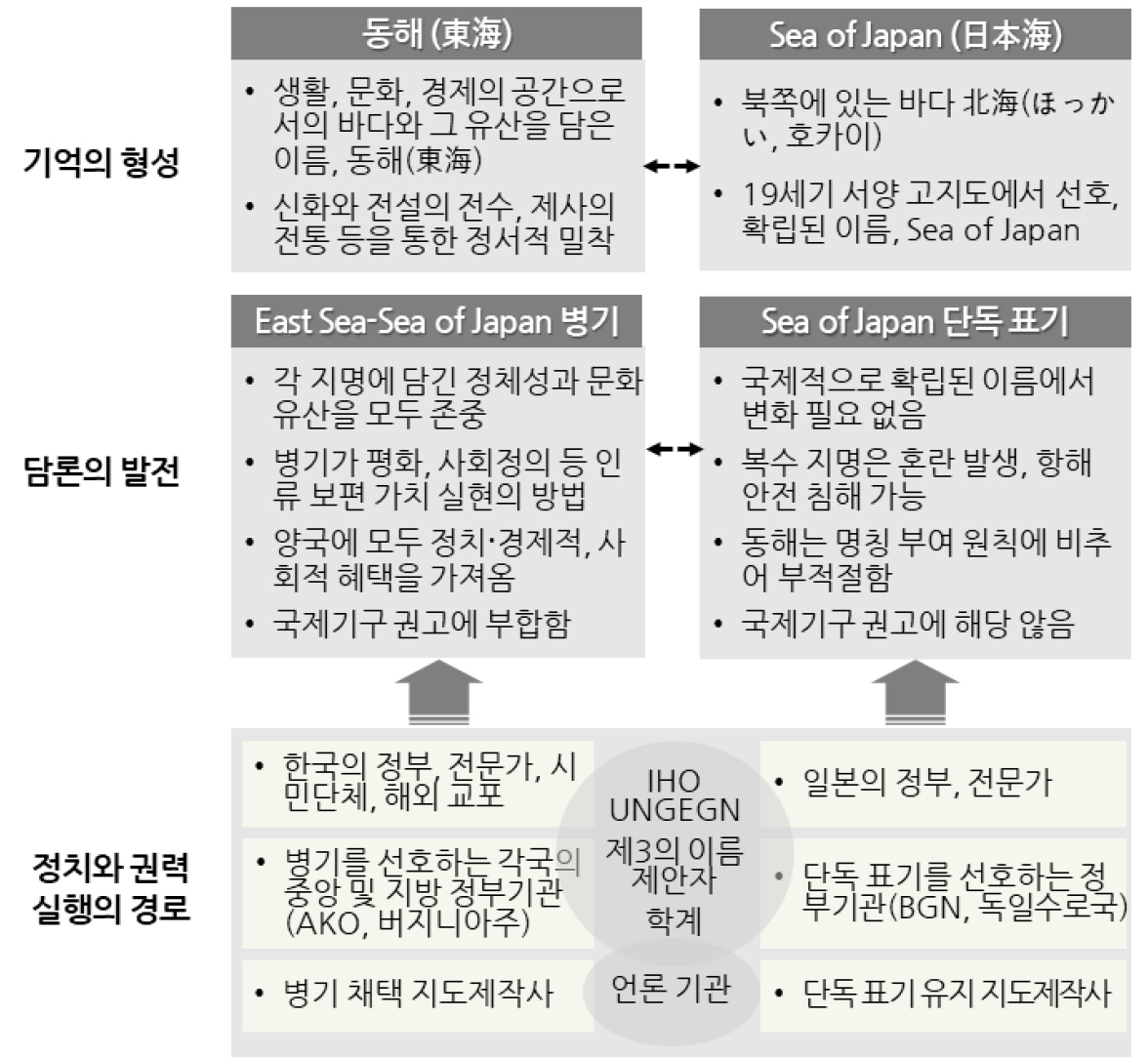
- 본 연구는 동해/일본해 표기 문제를 둘러싼 새로운 학술적 접근의 필요성에 주목하고, 선행 연구에서 지속가능한 지명 사용의 핵심 화두로 제기된 비판지명학의 관점을 적용하고자 하는 목적에서 출발하였다. 동해 수역의 표기는 관련 국가들이 상반된 논리와 주장을 명확한 입장 아래 전개하며, 전 세계 지명 사용자들이 다양한 방식으로 개입할 수밖에 없는 대표적 분쟁 지명이다. 이러한 특성은 지명의 제정・사용・변경 과정에 작동하는 권력 관계와 정치적 요소를 밝히는 데 초점을 두는 비판지명학의 시각을 적용할 충분한 정당성을 제공한다. 본 연구는 이 이슈를 이해하기 위한 분석 틀로서, 각 당사국의 입장에 반영된 장소 인식과 기억의 형성, 표기 방식의 정당성을 확보하기 위한 담론의 발전, 그리고 지명 사용과 선택에 영향을 미치는 정치・권력의 실행 경로를 설정하였다. 비판지명학적 관점을 동해/일본해 문제에 적용한 결과, 두 지명에 축적된 기억의 성격, 병기와 단독 표기를 둘러싼 논리 구조, 그리고 각 표기 방식을 선택하는 국가, 지도제작기관, 언론 등 다양한 지명 행위자의 의사결정 과정을 더욱 폭넓고 효율적으로 이해할 수 있는 분석적 기반이 마련된 것으로 판단된다.
- COLLAPSE
This study originates from the recognition that a new scholarly approach is needed to address the East Sea/Sea of Japan naming issue, and from the intention to apply the perspective of critical toponymy, which prior research has identified as a key framework for sustainable geographical naming. The naming of the East Sea is a representative case of a disputed toponym, as the states involved advance conflicting arguments based on clearly defined positions, while users of geographical names around the world inevitably participate in various ways in shaping or resolving the issue. These characteristics provide sufficient justification for applying critical toponymy, which focuses on uncovering the power relations and political dynamics at work in the creation, use, and alteration of geographical names. To analyze this issue, the study adopts a framework that examines: the formation of place perceptions and collective memories embedded in each country’s position and proposals; the development of discourses aimed at legitimizing particular naming practices; and the pathways through which political forces and power are exercised to influence the actors who use and determine place names. The application of a critical toponymic perspective to the East Sea/Sea of Japan dispute is found to enhance both the breadth and the analytical clarity with which we understand the memories tied to each name, the competing logics surrounding dual and single naming, and the decision-making processes of states, map producers, media organizations, and other actors involved in selecting between these naming conventions.
-
동해/일본해 표기 이슈에 대한 비판지명학의 시각
-
Research Article
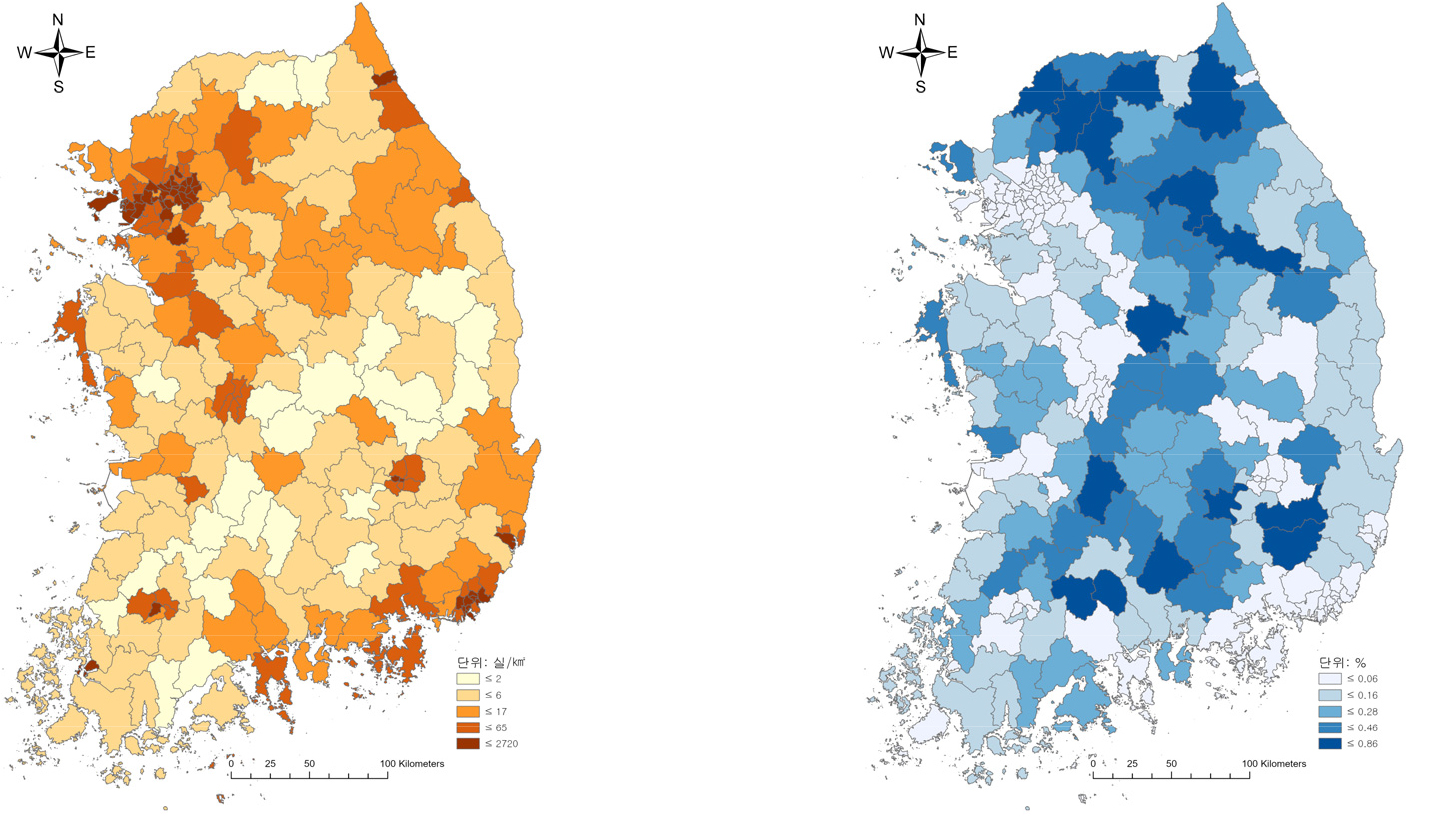
-
체류 관광과 야영장 공급 간 공간계량적 관계 분석 - 고유벡터 공간필터링(ESF)의 적용 -
Spatial Econometric Analysis of the Relationship Between Overnight Tourism and Campground Supply: An Application of Eigenvector Spatial Filtering
-
이서희, 전광상
Seo Hee Lee, Gwang-sang Jeon
- 최근 국내 관광 정책 및 학계 담론은 야영장업을 체류형 관광의 잠재적 인프라로 간주해 왔으며, 이에 따라 공공의 정책 지원과 민간 수요 확대 …
Recent tourism policy and scholarship in Korea have treated the camping sector as potential infrastructure for promoting longer-stay tourism. Against this backdrop, …
- 최근 국내 관광 정책 및 학계 담론은 야영장업을 체류형 관광의 잠재적 인프라로 간주해 왔으며, 이에 따라 공공의 정책 지원과 민간 수요 확대 아래 다수의 야영장 시설이 전국적으로 확산되었다. 이러한 배경에서 본 연구는 공간자료를 활용하여 야영장업의 공급 구조가 실제로 체류형 관광에 어떠한 영향을 미치는지 계량적으로 검증하고자 하였다. 2024년 기준 전국 226개 시군구의 평균 숙박일수를 종속변수로 설정하고 숙박 수용력 밀도, 야영장 비중을 주요 설명변수로, 이에 영향을 줄 수 있는 자원, 환경 및 지역적 특성을 통제변수로 정하여 고유벡터 공간필터링(ESF)을 주 분석모형으로 한 공간회귀분석을 실시하였다. 분석 결과, 숙박 수용력 규모와 야영장 비중이 높은 공급 구조는 기존의 정책적, 학문적 기대와 달리 평균 숙박일수를 단축시키는 방향으로 작용하였다. 이는 야영장의 단순 확대가 곧 체류형 관광의 활성화로 이어진다는 기존 정책적 가정을 재고할 필요가 있음을 시사한다.
- COLLAPSE
Recent tourism policy and scholarship in Korea have treated the camping sector as potential infrastructure for promoting longer-stay tourism. Against this backdrop, this study empirically examines how the spatial structure of campground supply affects the mean length of stay. Using 2024 cross-sectional data for 226 basic local governments, we model average overnight stays as a function of accommodation capacity density and the share of camping capacity, controlling for tourism resources, environmental conditions, and regional characteristics. Spatial regression models are estimated with eigenvector spatial filtering (ESF) adopted as the main specification. The results show that both larger accommodation capacity and a higher camping share are associated with shorter, rather than longer, stays, contrary to prevailing policy and academic expectations. This suggests that simply expanding campground supply is unlikely to activate stay-oriented tourism and that the policy assumption linking camping growth to longer stays needs to be reconsidered.
-
체류 관광과 야영장 공급 간 공간계량적 관계 분석 - 고유벡터 공간필터링(ESF)의 적용 -
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of the Korean Geographical Society
Journal of the Korean Geographical Society
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of the Korean Geographical Society
Journal of the Korean Geographical Society










